It’s not easy to be a farmer in Virginia. Pests, weather, uncertain markets and access to capital are a perennial problem. This year farmers have also had to contend with disruptions from President Donald Trump’s on-again, off-again tariffs, and an immigration crackdown that has deprived many farms of their experienced labor force.
And then there’s climate change and the outward creep of suburban sprawl. No wonder studies show the number of farms in Virginia continuing to shrink, and the age of farmers still in business trending steadily upward. We are losing our family farms.
That’s why I’m baffled by the resistance to solar in many parts of rural Virginia.
Farmers who lease part of their land for solar earn a guaranteed, stable income for 25 or 30 years, keep the property in the family, and never have to watch as a subdivision paves over the fields where they played as children. The income from a solar project will be there when a late frost means the loss of that year’s fruit crop or a scorching summer reduces the corn harvest by half.
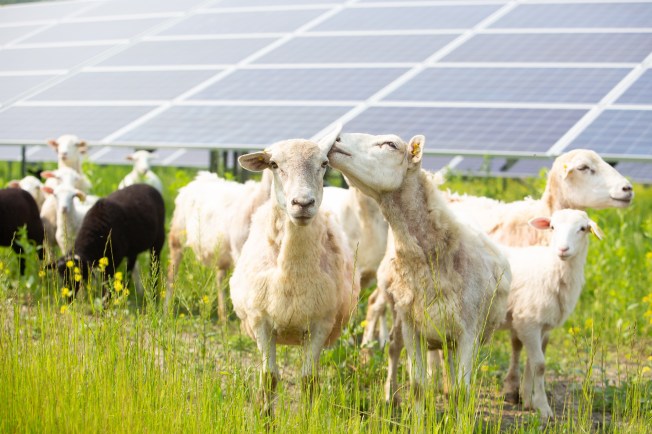
Indeed, these days the choice is not between farming and solar; farming and solar are increasingly compatible “crops.” Sheep grazing has gotten the most attention in Virginia for its perfect synergy with solar: the sheep thrive in the shade of the solar panels and do the work of vegetation management, which otherwise would require herbicides and machinery. Elsewhere, farmers are raising cattle, poultry, grapevines and shade-loving crops under solar, in a practice collectively known as agrivoltaics.
The combination of solar and agriculture is spreading rapidly across the country, endorsed by organizations like the American Farmland Trust. Solar sheep grazing is so popular that it has its own trade association, the American Solar Grazing Association. Here in Virginia, at least two sheep grazing companies contract with large solar developers for vegetation management. One, Gray’s Lambscaping, has over 800 sheep at solar projects, and expects to scale up to 5500 sheep by 2028.
Meanwhile, the conservation group Piedmont Environmental Council (PEC), which typically opposes large solar projects, is demonstrating the feasibility of growing vegetables under solar panels at a community farm in Loudoun County.
If solar integrates so well into the agricultural economy, what is the reasoning behind the county ordinances that ban solar or limit it to only a few projects? And why, when a county doesn’t prohibit solar outright, do local leaders so frequently reject permits for projects that meet all their conditions?
I’ve received emails from solar haters who regurgitate misinformation about the harms of solar panels, I’ve listened to legislators wax eloquent on the subject of “protecting rural values,” and I’ve sighed in frustration at a few fellow members of the environmental community who, when it comes to it, care less about addressing climate change than about keeping viewsheds pretty.
Often the opposition to solar is couched in terms of defending local control of land use decisions. But too many localities use this authority, not to make sure projects are developed responsibly, but to make sure they aren’t developed at all. And to that end, they prevent landowners from using their land in the way the owners have decided they need to. The rejections don’t mean the land returns to being farmed; more likely it means the land will be sold and, quite likely, developed for housing or even – gah! – data centers. If localities cared about saving farmland, they would approve more solar.
In the last year, the percentage of utility solar projects that receive permits from localities ticked up slightly. One possibility is that the hostility to solar is easing. That would be welcome, but I suspect the more likely reason is that solar companies aren’t pursuing projects where they expect rejection. That’s a loss all around: the localities lose out on tax revenue, their landowners lose out on income, and everyone loses out on low-cost electricity.
The hostility to solar makes little sense to me. Conservatives who care about property rights typically favor landowners over the government, so why is solar different? To be fair, some conservatives actively support solar, such as the groups Conservatives for Clean Energy and Energy Right.
On the other side of the political spectrum, liberals and everyone else who cares about climate change should want solar everywhere – and most do, but not all. As for solar and farming, those of any political persuasion who care about farmland preservation should favor solar over subdivisions. And anyone who cares about the farmers themselves should be spreading the gospel of solar. Agrivoltaics is just the icing on the cake that can make everyone feel they didn’t have to compromise.
The legislative response
Legislators have struggled with this problem for several years now. Many are desperate for new clean energy projects to serve the fast-rising demand for electricity, but they’ve been unable to bring themselves to take authority away from recalcitrant localities. It’s a hard needle to thread.
Last year members of the Commission on Electric Utility Regulation (CEUR) crafted a multi-part bill designed to give localities all the information they need to make rational decisions about solar permitting, while giving landowners and project developers a right to appeal adverse decisions to the State Corporation Commission (SCC).
That bill failed in committee, and this year only a part of it made it into a bill. House Bill 918, from Del. Rip Sullivan, D-Fairfax, sets up a university consortium to provide expertise and guidance, including on solar siting and permitting.
Meanwhile, a bill proposed last year by members of the solar industry came closer to passage than the CEUR bill did. The industry bill proposed a suite of rigorous best practices for solar, designed to reassure localities that solar facilities will be good neighbors.
Among the best practices were farm-friendly provisions like using native pollinator plants, screening with native trees, and incorporating grazing animals or farm crops. Localities would not be allowed to ban solar outright, but would have to make decisions on the merits of each proposal. However, nothing in the bill would have required localities to approve these projects.
The industry bill foundered last year, but this year it is back with the endorsement of CEUR. In its current form, HB 711 from Del. Charniele Herring, D-Alexandria, and Senate Bill 347 from Sen. Schuyler VanValkenburg, D-Henrico, continues to preserve local decision-making, but localities that deny permits to solar projects must report their reasons to the SCC for inclusion in a public database. SB 347 has already been reported from committee and will be heard by the full Senate.
Only one bill this year is directly aimed at helping farmers install solar. HB 1091 from Del. Amy Laufer, D-Albermarle, adds half a line to Virginia’s right-to-farm law giving farmers a right to install solar if they also use the same land for agricultural activities like grazing or crops. The effect of Laufer’s bill is that any farmer who wants to combine solar and farming could do so without having to go get a local permit. (The right-to-farm law does not exempt farmers from other laws, so regulations governing erosion, wetland protection, etc. still apply.)
A more modest bill, developed by PEC and carried by Del. Irene Shin, D-Fairfax, defines agrivoltaics and sets up an advisory panel to determine what qualifies, consider possible requirements and limitations, and make recommendations for next year. That’s encouraging, but unfortunately, the bill defines agrivoltaics specifically to exclude “solar energy generation that replaces the farmer’s primary income.”
Counterfactual definitions like this tend to cause problems.
If a farmer has a crop failure, and the farm’s major source of income that year is solar, do they no longer qualify? It also suggests that sheep graziers in the business of using their animals for vegetation management at solar projects – i.e., agrivoltaics – could not use the industry-accepted word to describe what they do. Besides, really, don’t we want all solar projects to incorporate agriculture?
A bill from Sen.David Marsden, D-Fairfax, would task the Department of Energy with setting up a committee of experts to develop solar siting criteria and then score the appropriateness of any proposed site for solar. There’s no indication in the bill that the criteria would include a farmer wanting to include solar among their products, but perhaps it could. However, it would not require localities to approve any projects.
It feels inevitable that the future of solar incorporates farming, and the future of farming may well mean incorporating solar. Whether Virginia’s leaders see this yet or not is another question, but they do have their opportunity this year.
This article was originally published in the Virginia Mercury on January 28, 2026.