Maybe it’s the heat. Heat-addled brains might explain the thinking of many Virginia lawmakers that what we need to do right now is burn more fossil fuels.
Scientists have documented the way high temperatures affect the brain, impairing cognition and causing impulsivity and trouble concentrating. And this summer is already starting out hot, which is saying something given that 2024 was the hottest year on record, bumping 2023 off its baking pedestal. Scientists say this global fever is the natural result of burning fossil fuels and driving CO2 levels to their highest in millions of years.
Since burning more fossil fuels will drive more global warming, it’s exactly the reverse of what we should be doing. Yes, but, these state leaders respond, how else are we going to power ever more data centers?
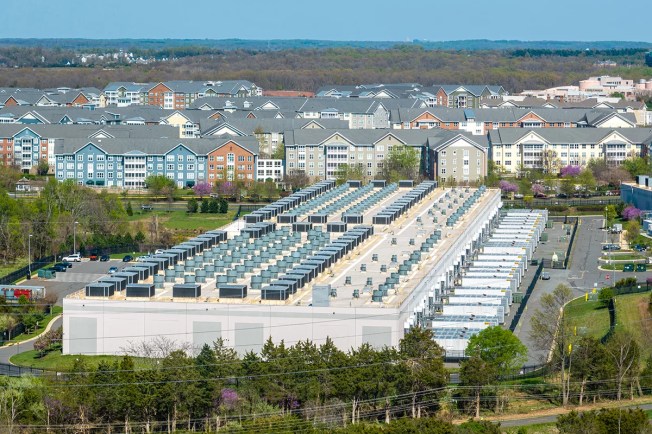
Northern Virginia is the data center capital of the world, and data centers are notoriously power-hungry. Without them, Virginia electricity demand would be flat, and we could easily meet our electricity needs while gradually decarbonizing along the pathway laid out in the Virginia Clean Economy Act (VCEA).
Instead, Virginia taxpayers subsidize some of the richest corporations in America to the tune of almost a billion dollarsevery year to entice them to rip up land in Loudoun, Prince William and other Virginia counties instead of Atlanta or Dallas. In return, the tech companies keep construction workers busy, underwrite their host counties’ finances, make life miserable for nearby residents, raise everyone’s power bills, drain our rivers and aquifers and pollute our air with enough diesel generators to light up a major city.
Virginia legislators obviously consider this a fair deal, because that’s what they keep voting for. Whether their constituents agree is another question; the evidence says they don’t.
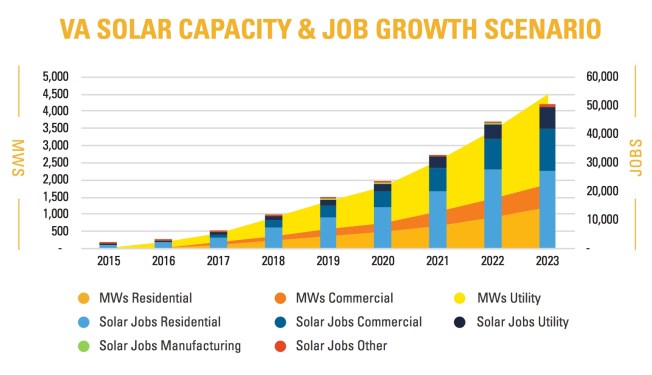
For anyone just getting up to speed on data center issues, the Virginia Sierra Club’s new report, “Unconstrained Demand: Virginia’s Data Center Expansion and Its Impacts” (to which I contributed), covers the current state of data center development in Virginia and the problems that come with it. Fun fact: More than half of all the nation’s energy consumption attributed to data centers occurs in Virginia.
That puts a special burden of leadership on our lawmakers. If we allow data centers to undermine our sustainability efforts here, we can only expect a race to the bottom in other states. As Virginia goes, so goes the nation.
And yet we haven’t heard much outcry from Virginia leaders against the plans of our largest utility to build new generating plants powered by fracked gas. Dominion Energy laid out its plans in its 2024 integrated resource plan as well as a proposal for a 944 megawatts of gas combustion turbines in Chesterfield now pending before the State Corporation Commission.
Dominion and its allies say more gas is needed for reliability, which could make it allowable under the VCEA. Indeed, “reliability” is a word that fossil fuel advocates frequently toss down like a trump card (in the unpresidential sense but with the same lack of thoughtful analysis). The claim is suspect. Fussing about reliability when your state ranks 24th in the nation for renewable energy is like worrying about the taxes you’ll owe if you win the lottery: we should be so lucky.
Gov. Glenn Youngkin and Republican legislators are explicit in wanting to see the VCEA repealed and more gas plants built. Democrats defend the VCEA’s goals, but worry about the challenges of implementation and the effect on electricity rates. They all cite data center demand as the reason they contemplate backsliding on clean energy.
I wish I could say that our rich and powerful tech companies were aggressively championing carbon-free energy for their data centers in Virginia, but they are not. I attended a meeting of the Commission on Electric Utility Regulation where legislators were hashing out the problems of too much demand and too little supply. Representatives from the Data Center Coalition stood in the back of the room, observing but refusing to engage. Out of sight, they successfully lobbied against any bills that would slow the data center boom, force them to absorb more of its costs, or require them to source their own clean energy.
Publicly, many tech companies tout their commitments to decarbonization. Amazon says it even met its goal to run its operations entirely on renewable energy. Yes, and I’m the Queen of Sheba. In fact, these companies are in a fierce competition to develop artificial intelligence as fast as possible. They’d like carbon-free power, but really, they’ll take whatever energy they can get wherever they can get it, and even among the industry’s best actors, climate now takes a back seat.
Yet the likes of Mark Zuckerberg and Jeff Bezos would not be significantly worse off if forced to meet their climate commitments. Virginia leaders know – or at any rate, they have been exposed to the information, which I realize is not the same thing – that building new fossil gas generating plants is not just bad for the planet but more expensive than pursuing carbon-free alternatives.
Oh, I know, Congress just yanked back the federal tax incentives that helped make wind and solar as cheap as it is, one of the myriad ill-considered elements of the big beautiful debt bomb Republicans adopted against everyone’s better judgment. (Apparently heat affects spines as well as brains.) With passage of that bill, developers will need to have begun construction on new facilities by this time next year in order to qualify for the existing tax credits.
There will be a mad rush to get construction underway immediately for facilities in the development pipeline. Thereafter, projects on the margin won’t get built. But others will, because even the loss of federal subsidies won’t destroy solar’s competitive edge against most new-build gas.
Even so, utilities and their customers will pay higher prices for unsubsidized new renewable energy – as well as for existing fossil fuel generation that will command higher prices in the coming supply crunch. The Clean Energy Buyers Association estimates that commercial electricity costs in Virginia will be about 10% higher after the phase-out of federal incentives.
A years-long backlog for orders of gas turbines will further squeeze energy supply and drive up prices for fossil power. On the plus side, the lack of available turbines will make fast-to-deploy solar not just the better option, but sometimes the only option.
I’ve never understood the conservative love affair with fossil fuels, when today’s clean technology is cleaner, cheaper and quicker to deploy. Trump would like to crush wind and solar altogether, which would eliminate 90% of the power capacity waiting to be connected to the grid and catapult the U.S into a serious energy crisis. In addition to much higher power prices, observers warn we would likely see a loss of data centers and other energy-intensive industries to parts of the world that are not on a mission to kill low-cost clean energy.
Well, that would be one way to rid Virginia of the data center scourge.
Fortunately, the worst attacks on solar in Trump’s budget bomb did not survive, but the bill should nonetheless serve as a wake-up call for Virginia leaders. With little time left to secure federal clean energy incentives, our utilities need to acquire all the solar and storage they can right now. With or without data centers, locking in as much fuel-free generation as possible while it’s available at a discount is a prudent move to avoid the coming shortages and escalating costs of energy.
As for the tech companies, lawmakers should embrace the simplest approach to this problem, which happens also to be the one that spares ordinary Virginians from bearing the costs of the data center buildout: shifting responsibility for sourcing electricity onto the companies themselves, and requiring that they live up to their climate claims by making the power they buy carbon-free.
It’s an approach other states can follow, holding Big Tech to the same responsibility no matter where they put their data centers. Certainly the tech titans can afford it; they just won big with massive tax cuts that our poorest residents will pay for.
No doubt they will complain. Everyone would like somebody else to pay for what benefits them. But Virginians can’t afford to subsidize Big Tech, and we don’t want to.
As for those legislators who think we should continue to do it anyway – well, all I can think is, it’s got to be the heat.
This article was originally published on July 8, 2025. On July 7, President Trump signed an executive order directing cabinet members to find more ways to hobble wind and solar energy, including directing the Secretary of the Treasury to interpret “beginning of construction” in a way that requires “a substantial portion” of a facility to have been built in order to qualify for tax incentives, counter to current regulation.